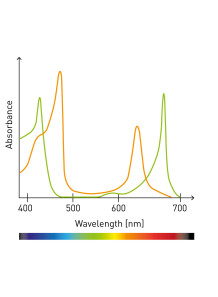
UV-VIS Anti-Tyrosinase Assay (L-Dopa)
- Product Code: 30980
Analysis of Anti-Tyrosinase Assay using L-DOPA
UV-VIS Anti-Tyrosinase Assay (L-Dopa, 1 sample)
Analysis of Anti-Tyrosinase Assay using L-DOPA
The use of L-DOPA (L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine) to test anti-tyrosinase activity is related to the field of enzymology and pharmacology, particularly in the study of substances that may inhibit the activity of the enzyme tyrosinase. Tyrosinase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the biosynthesis of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin, hair, and eye color in humans and the coloration of various tissues in other organisms. It catalyzes the conversion of L-tyrosine, an amino acid, into L-DOPA, which is an important intermediate in the melanin synthesis pathway.
Here's how L-DOPA is used to test anti-tyrosinase activity:
Tyrosinase Activity Assay: To study the inhibitory effects of a substance (eg, a chemical compound or natural extract) on tyrosinase activity, researchers typically perform a tyrosinase activity assay. This assay measures the rate at which tyrosinase converts L-tyrosine into L-DOPA in the presence or absence of the test substance.
L-DOPA as a Substrate: L-DOPA is used as a substrate in the tyrosinase assay. In the absence of any inhibitor, tyrosinase catalyzes the conversion of L-tyrosine into L-DOPA. This reaction produces a measurable change, often a color change, that can be detected and quantified using spectrophotometry or other analytical techniques.
Assessing Inhibition: When a potential anti-tyrosinase compound is introduced into the assay system, it may inhibit tyrosinase activity. If the substance is an effective inhibitor, it will reduce the rate of conversion of L-tyrosine to L-DOPA, leading to a slower or less pronounced color change.
Quantification: The degree of inhibition can be quantified by comparing the rate of L-DOPA formation in the presence of the inhibitor to the rate in its absence (control). This quantification provides information about the inhibitory potency of the tested substance.
Dose-Response Curve: Researchers often perform dose-response experiments where different concentrations of the inhibitor are tested to determine the concentration at which it exerts a significant inhibitory effect on tyrosinase activity. This allows the calculation of the inhibitory concentration (IC50), which represents the concentration of the inhibitor required to reduce enzyme activity by 50%.
| Step | Procedure | Expected Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Prepare Sodium... |
A clear buffer solution at pH 6.8 and 0.05 mM concentration. |
| 2 | Prepare... |
A homogeneous, clear L-tyrosine solution at 0.244 mM. |
| 3 | Prepare... |
A ready-to-use enzyme solution at 350 U/ml in sodium phosphate buffer. |
| 4 | Sample... |
A homogeneous sample solution at 1 mg/ml concentration. |
| 5 | Prepare Controls: •... |
Negative control with no inhibitory effect; positive control with known inhibitory activity. |
| 6 | Set... |
Each well contains 90 µl of the appropriate test or control solution. |
| 7 | Add Substrate... |
Each well now contains 290 µl total volume with the substrate included. |
| 8 | Add Enzyme... |
Reaction is initiated as enzyme contacts the substrate in each well. |
| 9 | Incubation: Incubate... |
Reaction proceeds under standardized temperature conditions for 10 minutes. |
| 10 | Measure Absorbance:... |
Absorbance values are recorded for each well (sample, negative control, and positive control). |
| 11 | Calculation of... |
Percentage inhibition values are obtained for each test sample and can be compared to the positive control’s inhibition result. |
You will receive a report for the % Inhibition of antityrosinase activity fields when we provide this service
Analysis of Anti-Tyrosinase Assay using L-DOPA
UV-VIS Anti-Tyrosinase Assay (L-Dopa, 1 sample)
Analysis of Anti-Tyrosinase Assay using L-DOPA
The use of L-DOPA (L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine) to test anti-tyrosinase activity is related to the field of enzymology and pharmacology, particularly in the study of substances that may inhibit the activity of the enzyme tyrosinase. Tyrosinase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the biosynthesis of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin, hair, and eye color in humans and the coloration of various tissues in other organisms. It catalyzes the conversion of L-tyrosine, an amino acid, into L-DOPA, which is an important intermediate in the melanin synthesis pathway.
Here's how L-DOPA is used to test anti-tyrosinase activity:
Tyrosinase Activity Assay: To study the inhibitory effects of a substance (eg, a chemical compound or natural extract) on tyrosinase activity, researchers typically perform a tyrosinase activity assay. This assay measures the rate at which tyrosinase converts L-tyrosine into L-DOPA in the presence or absence of the test substance.
L-DOPA as a Substrate: L-DOPA is used as a substrate in the tyrosinase assay. In the absence of any inhibitor, tyrosinase catalyzes the conversion of L-tyrosine into L-DOPA. This reaction produces a measurable change, often a color change, that can be detected and quantified using spectrophotometry or other analytical techniques.
Assessing Inhibition: When a potential anti-tyrosinase compound is introduced into the assay system, it may inhibit tyrosinase activity. If the substance is an effective inhibitor, it will reduce the rate of conversion of L-tyrosine to L-DOPA, leading to a slower or less pronounced color change.
Quantification: The degree of inhibition can be quantified by comparing the rate of L-DOPA formation in the presence of the inhibitor to the rate in its absence (control). This quantification provides information about the inhibitory potency of the tested substance.
Dose-Response Curve: Researchers often perform dose-response experiments where different concentrations of the inhibitor are tested to determine the concentration at which it exerts a significant inhibitory effect on tyrosinase activity. This allows the calculation of the inhibitory concentration (IC50), which represents the concentration of the inhibitor required to reduce enzyme activity by 50%.
| Mechanism | - |
| Appearance | - |
| Longevity | - |
| Strength | - |
| Storage | - |
| Shelf Life | - |
| Allergen(s) | - |
| Dosage (Range) | - |
| Recommended Dosage | - |
| Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Recommended Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Mix Method | - |
| Heat Resistance | - |
| Stable in pH range | - |
| Solubility | - |
| Product Types | - |
| INCI | - |
| Step | Procedure | Expected Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Prepare Sodium... |
A clear buffer solution at pH 6.8 and 0.05 mM concentration. |
| 2 | Prepare... |
A homogeneous, clear L-tyrosine solution at 0.244 mM. |
| 3 | Prepare... |
A ready-to-use enzyme solution at 350 U/ml in sodium phosphate buffer. |
| 4 | Sample... |
A homogeneous sample solution at 1 mg/ml concentration. |
| 5 | Prepare Controls: •... |
Negative control with no inhibitory effect; positive control with known inhibitory activity. |
| 6 | Set... |
Each well contains 90 µl of the appropriate test or control solution. |
| 7 | Add Substrate... |
Each well now contains 290 µl total volume with the substrate included. |
| 8 | Add Enzyme... |
Reaction is initiated as enzyme contacts the substrate in each well. |
| 9 | Incubation: Incubate... |
Reaction proceeds under standardized temperature conditions for 10 minutes. |
| 10 | Measure Absorbance:... |
Absorbance values are recorded for each well (sample, negative control, and positive control). |
| 11 | Calculation of... |
Percentage inhibition values are obtained for each test sample and can be compared to the positive control’s inhibition result. |
Cart
No products