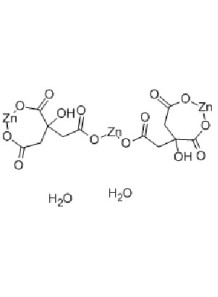
Zinc Citrate (31% Zinc)
- Product Code: 9222
a form of zinc that is often used in dietary supplements and fortification of food products. It is known for its high bioavailability
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
| Test Name | Specification |
|---|---|
| Assay | 98.5% Minimum |
| Appearance | White crystal powder |
| Identification | Positive |
| Acidity | Pass |
| Alkalinity | Pass |
| Loss on Drying | 6.5% Maximum |
| Iron | 0.005% Maximum |
| Lead | 0.001% Maximum |
| Arsenic | 0.0002% Maximum |
| Zinc (w/%) | 31.3 Min |
Zinc citrate is a form of zinc that is often used in dietary supplements and fortification of food products. It is known for its high bioavailability, which means it is easily absorbed by the body. Here are some health benefits of zinc citrate:
-
Immune System Support: Zinc is essential for maintaining a healthy immune system. It helps in the development and function of immune cells and has been shown to reduce the duration and severity of colds and other infections.
-
Wound Healing: Zinc plays a critical role in wound healing and skin health. It is involved in collagen synthesis, immune function, and inflammatory response, all of which are crucial for proper wound healing.
-
Antioxidant Properties: Zinc acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals. This can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases associated with oxidative stress, such as heart disease and cancer.
-
Growth and Development: Zinc is necessary for proper growth and development, especially during childhood, adolescence, and pregnancy. It supports cell division, protein synthesis, and DNA synthesis.
-
Skin Health: Zinc is beneficial for various skin conditions, including acne, eczema, and psoriasis. It regulates oil gland activity, promotes the production of new skin cells, and has anti-inflammatory properties.
-
Reproductive Health: Zinc is important for reproductive health in both men and women. It plays a role in hormone production, including testosterone, and is essential for sperm production and ovulation.
-
Taste and Smell: Zinc is necessary for the proper functioning of the senses of taste and smell. Zinc deficiency can lead to a loss of these senses.
-
Blood Sugar Regulation: Zinc plays a role in insulin production and secretion, helping to regulate blood sugar levels. This can be particularly beneficial for people with diabetes.
-
Cognitive Function: Zinc is involved in brain function and cognitive development. It supports neurotransmitter function and can help improve memory and learning.
-
Eye Health: Zinc is essential for maintaining healthy vision. It helps transport vitamin A from the liver to the retina, where it is used to produce melanin, a protective pigment in the eyes.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Zinc has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce the symptoms of chronic inflammatory diseases.
Be the first to review this product :-)
Recommend Lab-Service
| Lab Service | Price |
|---|
a form of zinc that is often used in dietary supplements and fortification of food products. It is known for its high bioavailability
Zinc citrate is a form of zinc that is often used in dietary supplements and fortification of food products. It is known for its high bioavailability, which means it is easily absorbed by the body. Here are some health benefits of zinc citrate:
-
Immune System Support: Zinc is essential for maintaining a healthy immune system. It helps in the development and function of immune cells and has been shown to reduce the duration and severity of colds and other infections.
-
Wound Healing: Zinc plays a critical role in wound healing and skin health. It is involved in collagen synthesis, immune function, and inflammatory response, all of which are crucial for proper wound healing.
-
Antioxidant Properties: Zinc acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals. This can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases associated with oxidative stress, such as heart disease and cancer.
-
Growth and Development: Zinc is necessary for proper growth and development, especially during childhood, adolescence, and pregnancy. It supports cell division, protein synthesis, and DNA synthesis.
-
Skin Health: Zinc is beneficial for various skin conditions, including acne, eczema, and psoriasis. It regulates oil gland activity, promotes the production of new skin cells, and has anti-inflammatory properties.
-
Reproductive Health: Zinc is important for reproductive health in both men and women. It plays a role in hormone production, including testosterone, and is essential for sperm production and ovulation.
-
Taste and Smell: Zinc is necessary for the proper functioning of the senses of taste and smell. Zinc deficiency can lead to a loss of these senses.
-
Blood Sugar Regulation: Zinc plays a role in insulin production and secretion, helping to regulate blood sugar levels. This can be particularly beneficial for people with diabetes.
-
Cognitive Function: Zinc is involved in brain function and cognitive development. It supports neurotransmitter function and can help improve memory and learning.
-
Eye Health: Zinc is essential for maintaining healthy vision. It helps transport vitamin A from the liver to the retina, where it is used to produce melanin, a protective pigment in the eyes.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Zinc has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce the symptoms of chronic inflammatory diseases.
| Mechanism | - |
| Appearance | - |
| Longevity | - |
| Strength | - |
| Storage | - |
| Shelf Life | - |
| Allergen(s) | - |
| Dosage (Range) | - |
| Recommended Dosage | - |
| Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Recommended Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Mix Method | - |
| Heat Resistance | - |
| Stable in pH range | - |
| Solubility | - |
| Product Types | - |
| INCI | - |
Cart
No products