For Research Only
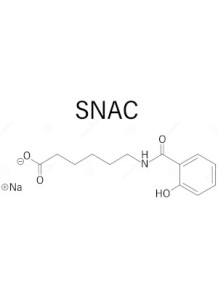
Salcaprozate Sodium (SNAC) is a sodium salt of salcaprozic acid, commonly used as an absorption enhancer in pharmaceutical formulations. It improves the bioavailability of poorly absorbed drugs by facilitating their transport across biological membranes, particularly in the gastrointestinal tract. SNAC is often utilized in oral drug delivery systems to enhance the absorption of peptides, proteins, and other large molecules that typically have low oral bioavailability.
Key Features and Applications:
Absorption Enhancer: SNAC works by temporarily increasing the permeability of the intestinal epithelium, allowing larger molecules to pass through more effectively.
Oral Delivery: It is particularly useful in oral formulations of drugs that are otherwise administered via injection, such as certain peptides and proteins.
Stability: SNAC can also protect drugs from degradation in the harsh environment of the stomach, improving their stability and efficacy.
Mechanism of Action:
SNAC enhances drug absorption through several mechanisms:
Chelation: It can chelate calcium ions, which are involved in maintaining tight junctions between epithelial cells. This chelation temporarily loosens these junctions, allowing for paracellular transport of drugs.
Surfactant Properties: SNAC can act as a surfactant, reducing the surface tension and improving the solubility and dispersibility of drugs.
Mucosal Interaction: It may interact with the mucosal layer, altering its viscosity and facilitating drug penetration.
Clinical Applications:
SNAC has been used in various clinical settings, including:
Oral Semaglutide: SNAC is a key component in the formulation of oral semaglutide (Rybelsus), a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. This formulation allows for the oral administration of semaglutide, which would otherwise require injection.
Other Peptide Drugs: Research is ongoing to explore the use of SNAC in the oral delivery of other peptide-based drugs, potentially expanding the range of treatments available in oral form.
Safety and Regulatory Status:
SNAC has been evaluated for safety in various clinical trials and is generally considered safe for use in pharmaceutical formulations. It has received regulatory approval for use in specific drug products, such as oral semaglutide, by agencies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
Research and Development:
Ongoing research aims to further optimize the use of SNAC in drug delivery systems, exploring its potential in enhancing the absorption of a wider range of therapeutic agents. This includes investigating its use in combination with other absorption enhancers and novel drug delivery technologies.
In summary, Salcaprozate Sodium (SNAC) is a valuable tool in the development of oral drug delivery systems, particularly for enhancing the bioavailability of peptides and proteins. Its ability to improve drug absorption and stability makes it a key component in the formulation of innovative therapeutic products.