Vitamin E Calcium Succinate
a stable ester form of vitamin E with properties different from alpha-tocopherol or alpha-tocopheryl acetate.
Cart
No products
No products
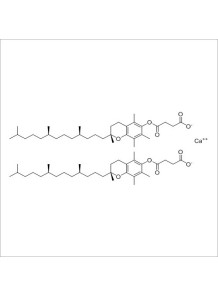
a stable ester form of vitamin E with properties different from alpha-tocopherol or alpha-tocopheryl acetate.
What is Vitamin E Calcium Succinate?
Vitamin E Calcium Succinate is a compound combining:
Vitamin E (as Alpha-Tocopheryl Succinate) – a stable ester form of vitamin E with properties different from alpha-tocopherol or alpha-tocopheryl acetate.
Calcium – an essential mineral.
Succinate (Succinic Acid) – a metabolic intermediate in the Krebs cycle (energy production in cells).
While each component has established benefits, the combined salt form primarily serves as a delivery system. There is limited research indicating unique synergistic effects beyond delivering vitamin E and calcium together.
Antioxidant (Indirect Effect):
VES itself is not a strong antioxidant, but once hydrolyzed in the body, it releases alpha-tocopherol, a potent fat-soluble antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative damage.
Traber MG & Atkinson J. (2007). Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 43(1), 4–15.
Anti-Cancer Potential (Preclinical Evidence):
VES has been studied for its ability to induce apoptosis (cell death), reduce proliferation, and block angiogenesis in cancer cells.
Shiau CW et al. (2013). J Cell Physiol, 228(4), 764–772.
Neuzil J et al. (2001). Apoptosis, 6(1–2), 31–47.
Note: These are preclinical studies. There’s no clinical proof yet that VES can treat or prevent cancer in humans.
Immune Modulation:
Vitamin E may support immune function. This is well-established for alpha-tocopherol; data on VES is limited.
Bone Health: Supports strong bones and teeth, and helps prevent osteoporosis.
Institute of Medicine (2011). Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D.
Muscle Function & Nerve Transmission
Blood Clotting: Required for normal coagulation.
Energy Metabolism: As part of the Krebs cycle, succinate contributes to energy production. However, supplementation doesn’t necessarily enhance energy in healthy individuals.
| Mechanism | - |
| Appearance | - |
| Longevity | - |
| Strength | - |
| Storage | - |
| Shelf Life | - |
| Allergen(s) | - |
| Dosage (Range) | - |
| Recommended Dosage | - |
| Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Recommended Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Mix Method | - |
| Heat Resistance | - |
| Stable in pH range | - |
| Solubility | - |
| Product Types | - |
| INCI | - |