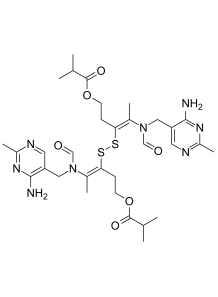
Sulbutiamine (e.q. Arcalion, Enerion, Sulbuxin)
a synthetic derivative of thiamine (vitamin B1), composed of two modified thiamine molecules linked together. Its main distinguishing feature is its lipid solubility, which allows it to cross the blood-brain barrier more effectively than standard thiamine.
ONLY FOR RESEARCH/ANALYTICAL WORK - THAILAND FDA DOES NOT YET ALLOWED TO USE IN FOOD
What is Sulbutiamine?
Sulbutiamine is a synthetic derivative of thiamine (vitamin B1), composed of two modified thiamine molecules linked together. Its main distinguishing feature is its lipid solubility, which allows it to cross the blood-brain barrier more effectively than standard thiamine. It was first developed in Japan for treating thiamine deficiency (beriberi) and symptoms such as fatigue (asthenia). Today, it is available as a prescription medication (e.g., Arcalion) in some countries, and as an over-the-counter dietary supplement in others (e.g., the United States).
Potential Health Benefits and Research
Note: While some studies support its benefits, much of the research is older, limited in scope, or focused on specific patient populations. Large-scale trials in healthy individuals are lacking.
1. Asthenia (Fatigue and Weakness)
Claim: Sulbutiamine may reduce fatigue, especially chronic or post-infectious types.
Evidence:
-
Tiev K., Cabane J., Imbert J.C. (1999). Traitement de l'asthénie post-infectieuse par le sulbutiamine. Revue de médecine interne, 20(10), 912–918.
→ A double-blind, placebo-controlled study found Sulbutiamine significantly more effective than placebo in reducing post-infectious fatigue.
-
Shah S.N. (2003). Adjuvant role of vitamin B analogue (sulbutiamine) with anti-infective treatment in infection-associated asthenia. J Assoc Physicians India, 51, 891–895.
→ Suggests Sulbutiamine improved recovery from fatigue when combined with anti-infective treatment.
-
Bizot J.C. et al. (2005). Chronic treatment with sulbutiamine improves memory in an object recognition task.... Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry, 29(6), 928–935.
→ In rats, Sulbutiamine reduced behavioral inhibition—relevant to motivation and fatigue.
2. Memory and Cognitive Function
Claim: Often promoted as a nootropic for improving memory and focus.
Evidence:
-
Micheau J. et al. (1985). Chronic administration of sulbutiamine improves long term memory formation in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 23(2), 195–198.
→ Animal study suggests memory improvements, possibly via cholinergic modulation.
-
Ollat H. et al. (1998). Effects of sulbutiamine on psycho-behavioural inhibition in major depressive episodes. Encephale, 24(3), 209–214.
→ Found improvements in attention and cognitive processing speed.
-
Séverin P., Jean-Marie V. (2003). Effects of sulbutiamine on cognitive function... in patients with mild cognitive impairment. European Psychiatry, 18(Suppl 1), 123.
→ Abstract suggests potential benefit, though full data and replication are needed.
Overall: Evidence for cognitive enhancement in healthy individuals is anecdotal or animal-based. Human data are limited and mostly focused on clinical deficits (e.g., dementia, depression).
3. Mood and Psycho-Behavioral Inhibition
Claim: May reduce inhibition and improve mood in conditions like depression.
Evidence:
-
Lôo H. et al. (2000). Effects of sulbutiamine on psycho-behavioral inhibition in major depressive episodes. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry, 24(1), 77–89.
→ Found significant improvements in emotional blunting, lack of drive, and physical retardation when used alongside antidepressants.
4. Erectile Dysfunction (Psychogenic Origin)
Claim: May help treat erectile dysfunction caused by psychological factors.
Evidence:
-
Dmitriev D.M., Gamidov V.V., Permiakova T.V. (2005). Clinical Efficacy of Arcalion in Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction. Urologiia, (4), 32–35.
→ A Russian study reported positive results, especially for psychogenic ED, though methodological concerns remain.
5. Thiamine Deficiency
Claim: Effective in treating thiamine deficiency (e.g., beriberi, Wernicke’s encephalopathy).
Evidence:
-
Sulbutiamine was originally created to address neurological and systemic consequences of deficiency, with better absorption and central nervous system (CNS) delivery than thiamine.
-
Standard thiamine remains effective for typical deficiency; Sulbutiamine may be more suitable in cases of malabsorption or CNS-specific need.