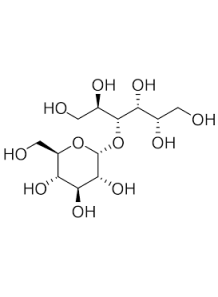
Maltitol
Food
Code: 36043
a sugar alcohol used as a sugar substitute in various food products
Cart
No products
Subtotal:
0.00
Total
0.00
THB