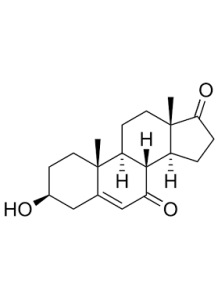
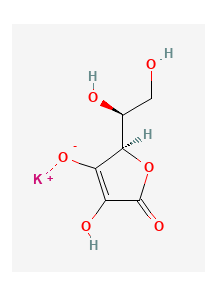
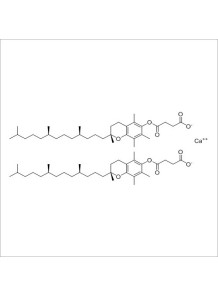
a naturally occurring metabolite of DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone). Unlike DHEA, it does not convert into sex hormones such as testosterone or estrogen, which means it is less likely to cause hormone-related side effects. Its primary proposed mechanism is increasing metabolic rate through thermogenesis—the body’s process of generating heat and burning calories.
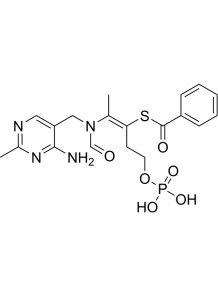
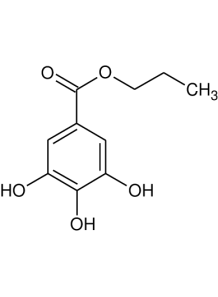
a synthetic, fat-soluble derivative of thiamine (vitamin B1). Its structure allows for greater absorption and cellular uptake compared to water-soluble thiamine, leading to higher intracellular levels. This enhanced bioavailability has prompted research into its therapeutic potential, especially for conditions related to high blood sugar and oxidative stress.
small shrimp extract Natural nutrients from the depths of the sea that many people may not be familiar with. But did you know that there are many benefits of this extract, especially those with high blood lipid problems?
type 50% Phospholipids, 25% Omega-3, 250ppm Astaxanthin , 15% EPA, 9% DHA
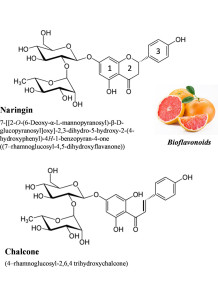
It is considered a super food because it contains a variety of substances that are beneficial to the body, such as amino acids, rutin, quercetin, vitamins A, B and C, and flavonoids. with antioxidant effects and with various substances
can dissolve in clear water
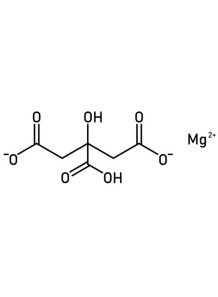
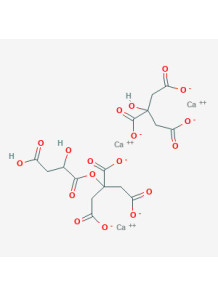
It is an acid that is important for the synthesis of nucleic acids, RNA-DNA, which are substances that are very necessary for cell reproduction and growth. If this substance is lacking, it will cause growth to slow down, stop or cause abnormalities. Especially in the fetus
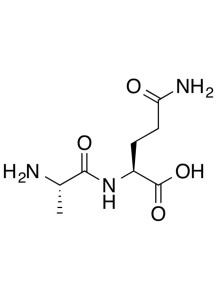
Folic acid (Folic Acid, 99%) is often called Vitamin B9.
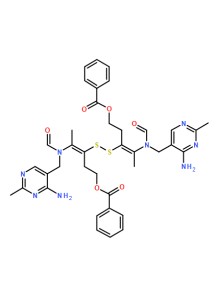
a synthetic, lipid-soluble derivative of thiamine (vitamin B1). Unlike standard water-soluble forms such as thiamine hydrochloride or mononitrate, bisbentiamine offers improved bioavailability, especially at higher doses. Its lipid-soluble nature allows it to potentially cross the blood-brain barrier more effectively and achieve higher thiamine concentrations in blood and tissues, including the brain.
Cart
No products