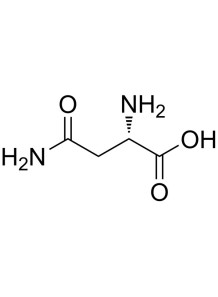
non-essential amino acids This means that the body can synthesize it on its own. Although L-asparagine is not generally considered essential in the diet due to the body's ability to produce it, But it plays many roles in maintaining health
L-AsparagineL-Asparagine It is a non-essential amino acid. This means that the body can synthesize it on its own. Although L-asparagine is not generally considered essential in the diet due to the body's ability to produce it, But it plays many roles in maintaining health:
Protein synthesis: It is the building block of protein. Involved in the synthesis of proteins that are essential for the structure and function of tissues, organs, enzymes, and the immune system.
Neurotransmitter Function: L-Asparagine It is a precursor to aspartate. which involves the synthesis of neurotransmitters in the brain Neurotransmitters are chemicals that transmit signals between nerve cells and are important for proper brain function.
Ammonia Detoxification: L-Asparagine Related to the urea cycle which plays a role in detoxifying ammonia which is a waste product produced during the breakdown of protein The urea cycle helps convert ammonia into urea. which can be excreted through the kidneys
Cellular activity: L-asparagine Is important to the functioning of various cells. Including maintaining the structure and integrity of cells. Helps balance absorption within cells and helps control cell volume.
Immune system support: Amino acids, including L-asparagine. Plays a role in supporting the immune system Involved in the production of antibodies and other components. of the immune system response
Energy Metabolism: L-Asparagine It contributes to energy metabolism by participating in the citric acid cycle. which is a series of chemical reactions that occur in cells to create energy from nutrients