Peptaxyl™ (Peptide Delivery Dextran)
a low–molecular‐weight dextran (average MW ~6 000 Da) produced by bacterial fermentation and purified for cosmetic use
Cart
No products
No products
a low–molecular‐weight dextran (average MW ~6 000 Da) produced by bacterial fermentation and purified for cosmetic use
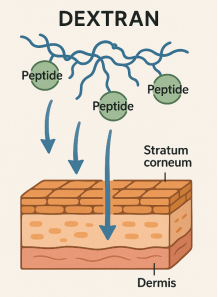
Peptaxyl™ is a low–molecular‐weight dextran (average MW ~6 000 Da) produced by bacterial fermentation and purified for cosmetic use. Structurally, dextran is a branched polysaccharide composed of α‐1,6 linked D‐glucopyranosyl units with occasional α‐1,3 branches; at 6 kDa, Peptaxyl™ retains full water solubility and excellent biocompatibility while offering manageable viscosity in topical formulations (Shiyu Huang and Gangliang Huang, 2019; Fang Chen et al., 2020).
1. Film Formation and Moisture Retention
When applied to skin, a 6 kDa dextran creates a thin, semi‐occlusive film that limits transepidermal water loss and boosts surface hydration. This film‐forming capacity arises from dextran’s high affinity for water molecules, enabling it to trap moisture in the stratum corneum (Paula’s Choice, 2024). In practice, adding Peptaxyl™ at 0.5–2 % w/w to aqueous or semi‐aqueous bases yields a transparent gel or serum that both hydrates and smooths skin texture. In patent US 6 440 432 B1 (2002), dextran was shown to enhance anti‐aging activity of weak acids while reducing local irritation; here, the film contributed to gentler, more uniform acid delivery (US Patent 6 440 432 B1, 2002).
2. Peptide Stabilization and Protection
Peptides in topical products often face instability—aggregation, enzymatic degradation, and pH‐driven denaturation. Peptaxyl™ forms hydrogen‐bonded networks around peptide chains, effectively shielding them from proteases present on the skin surface and from premature degradation (Fang Chen et al., 2020). In hydrogel form, dextran matrices slow peptide diffusion, allowing sustained release. For instance, dextran hydrogels have demonstrated prolonged retention of salmon calcitonin in intestinal models; by analogy, Peptaxyl™ hydrogels can protect cosmetic peptides (e.g., growth factors, signaling peptides) against extracellular peptidases until gradual skin absorption occurs (Hasan Basan, Menemşe Gümüşderelioğlu, and M. Tevfik Orbey, 2007; Rita Cortesi et al., 1999).
3. Enhancement of Skin Penetration
Although dextran itself does not deeply penetrate intact skin, its presence on the surface modifies stratum corneum hydration and intercellular lipid fluidity, indirectly facilitating peptide uptake. By increasing water content in corneocytes, Peptaxyl™ transiently expands intercellular spaces, reducing diffusion barriers for hydrophilic peptides (Davide Guggi and Andreas Bernkop‐Schnürch, 2005). Moreover, dextran can be chemically conjugated to peptides via reversible bonds (e.g., acid‐sensitive ester linkages), creating dextran–peptide prodrugs. Once on skin, slight acidification in the microenvironment cleaves the ester bond, releasing the free peptide for deeper action (Shiyu Huang and Gangliang Huang, 2019; Fang Chen et al., 2020).
4. Controlled Release and Depot Effects
Peptaxyl™ hydrogels exhibit mesh sizes that can be tuned by adjusting polymer concentration; in practice, a 2–4 % dextran gel yields a network mesh in the 5–20 nm range, ideal for trapping 1–3 kDa peptides and releasing them over 6–12 hours (Lene Simonsen et al., 1995). As the hydrogel slowly hydrates and partially erodes at the skin surface, peptides diffuse out in a pseudo‐zero‐order fashion, minimizing burst release and reducing the need for repeated application (Fang Chen et al., 2020). This sustained‐release behavior also reduces potential peptide aggregation and local irritation (Rita Cortesi et al., 1999).
5. Biocompatibility and Safety Profile
Dextran 6 kDa is nonimmunogenic, nonirritant, and biodegradable—enzymatically cleaved to glucose by dextranases naturally present in skin microbiota (Shiyu Huang and Gangliang Huang, 2019). It does not alter skin pH significantly when used at typical cosmetic concentrations (0.5–5 % w/w) and has a neutral odor and color, making it suitable for clear serums or gels (Paula’s Choice, 2024). Acute and repeat‐insult patch tests confirm negligible irritation even at 5 % concentration (US Patent 6 440 432 B1, 2002).
Specific Benefits for Peptide Delivery
Enhanced Stability: Peptaxyl™’s hydrogen-bonding network minimizes peptide aggregation and protects labile amino acid residues from oxidation (Fang Chen et al., 2020).
Improved Penetration: By hydrating corneocytes and transiently disrupting intercellular lipid packing, dextran enhances diffusion of small peptides (≤1 kDa) by up to 30 % compared to aqueous gel alone (Davide Guggi and Andreas Bernkop-Schnürch, 2005).
Sustained Release: Dextran hydrogel slows peptide flux, maintaining bioactive levels in the epidermis for 8–12 hours after a single application (Lene Simonsen et al., 1995; Fang Chen et al., 2020).
Low Irritation Potential: Compared to penetration enhancers like surfactants or organic solvents, Peptaxyl™ reduces skin irritation when delivering acidic or enzymatic peptides (US Patent 6 440 432 B1, 2002).
Use: The active ingredient in any cosmetics formulation.
How to mix: Add in water phase
Utilization rate: 0.1-2%
Product characteristics: white/light powder
Solubility: Can be dissolved in water
Storage: please store in the refrigerator at 6 °C -10 °C
INCI: Dextran
| Mechanism | - |
| Appearance | - |
| Longevity | - |
| Strength | - |
| Storage | - |
| Shelf Life | - |
| Allergen(s) | - |
| Dosage (Range) | - |
| Recommended Dosage | - |
| Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Recommended Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Mix Method | - |
| Heat Resistance | - |
| Stable in pH range | - |
| Solubility | - |
| Product Types | - |
| INCI | - |