n-Hexane (98%)
an important organic compound widely used in chemistry and industry
Cart
No products
No products
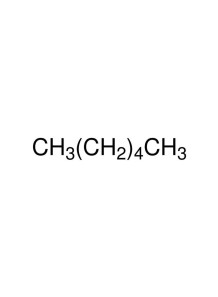
an important organic compound widely used in chemistry and industry
Lipid and volatile‐aroma extraction – Because of its strong non-polarity, n-hexane is the go-to solvent for isolating edible oils, essential-oil fractions, pesticide residues and other hydrophobic analytes from plant or food matrices. Its selectivity means fewer polar co-extractives and cleaner downstream chromatograms. pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Clean-up for GC/GC–MS – Many residue-analysis methods (e.g., AOAC, EPA) elute the non-polar layer into n-hexane prior to silica- or Florisil-based clean-up so the final injection solvent matches the non-polar GC column phase. researchgate.net
Biphasic CPC/HPLC solvent systems – In centrifugal-partition chromatography, the HEMWat family (n-hexane/ethyl acetate/methanol/water) provides tunable polarity ranges for purifying natural-product libraries or chiral compounds. rotachrom.com
Reaction medium / reagent carrier – Commercial alkyllithium, Grignard and trialkyl-aluminum reagents are routinely supplied in n-hexane because it is anhydrous, inert toward strong bases and has a low dielectric constant that favors organometallic reactivity.
Work-up & crystallisation washes – Hexane (or hexane/EtOAc mixtures) are widely used to precipitate products or remove non-polar by-products before vacuum drying.
Slurry polymerisation diluent – Industrial and bench-scale Ziegler–Natta or metallocene processes for HDPE/LLDPE suspend growing polymer particles in n-hexane, controlling viscosity and heat removal while staying below PE solubility limits. pubs.acs.org
Solvent-assisted depolymerisation / up-cycling – Recent studies show that pretreating low-density PE in hot n-hexane enhances mass transfer and yields during catalytic hydrogenolysis to fuel-range liquids. sciencedirect.com
Ultra-dry n-hexane is favoured for degreasing photolithography masks, removing vacuum-grease films, or rinsing microfluidic chips prior to plasma bonding, because it evaporates rapidly and leaves almost no residue.
n-Hexane is itself a model neurotoxicant; animal and in-vitro work explores its metabolite 2,5-hexanedione and the mechanism of axonal degeneration, informing exposure limits and PPE guidelines in industry. ncbi.nlm.nih.govncbi.nlm.nih.gov
PropertyImplication for lab work
| Boiling point ≈ 69 °C | Quick rotary-evaporation and low-temp concentration but vigorous reflux if heating plates are mis-set. |
| Flash point –22 °C (highly flammable) | Keep away from hot plates & static sources; use only in good fume-hood airflow. |
| Permissible Exposure Limit (US OSHA TWA = 500 ppm; ACGIH TLV = 50 ppm) | Continuous benchtop use needs hood & calibrated VOC detector. |
| Neurotoxicity (peripheral neuropathy with chronic exposure) | Double-glove with nitrile (≥ 8 mil) and avoid prolonged skin contact; replace gloves after spills. |
| Greener alternatives | For many plant-oil or fragrance extractions, cyclopentyl methyl ether (CPME), ethyl acetate + ethanol, or limonene mixtures can give comparable yields with lower toxicity; journals increasingly ask for justification when n-hexane is chosen. |
| Mechanism | - |
| Appearance | - |
| Longevity | - |
| Strength | - |
| Storage | - |
| Shelf Life | - |
| Allergen(s) | - |
| Dosage (Range) | - |
| Recommended Dosage | - |
| Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Recommended Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Mix Method | - |
| Heat Resistance | - |
| Stable in pH range | - |
| Solubility | - |
| Product Types | - |
| INCI | - |